Stroke
Home » Stroke
What is stroke, causes and how can it be prevented?
A stroke actually happens when a part of the brain does not get the oxygen it requires because the flow of blood to the brain (which provides oxygen to the brain) is cut off or a blood vessel bursts. Brain cells start to die without oxygen, and this can lead to death or permanent disability.
Stroke Causes:
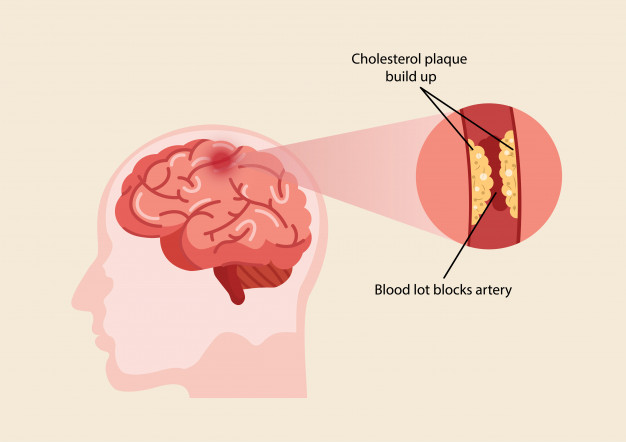
The two main signs of stroke are called ischemic or hemorrhagic, affecting the brain’s blood vessels.Ischemic strokes make up between 80% to 85% of all strokes and are caused when a blood vessel in the brain gets clogged with a clot just like the clogged arteries in the chest. When a blood vessel in the brain actually bursts and leaks, a hemorrhagic stroke is caused.
There are hemorrhagic strokes tend to be more serious. When deciding the medication used to help the patient, the difference between these two types of stroke can be important.
Schemic stroke ;Even the most common type of stroke occurs when blood is blocked from entering the brain, often because the artery is blocked by fatty deposits (atherosclerosis) or blood clotting.
Haemorrhagic stroke: When a blood vessel in the brain bursts and blood bleeds into the brain, this form of stroke occurs. It may also be caused by an aneurysm — a thin or weak spot in an artery that can burst out of balloons.
Some other symptoms of a stroke could be:
- Numbness of the face
- Lack of vision
- Gait shift
- Face drooping
- Difficulty in speech
- Weakness -arms
- Blurry vision
- Numbness
- Severe headache
Stroke is treatable:
Stroke is a medical issue that is complicated. But there are ways to reduce its effect dramatically. Recognizing stroke symptoms early, treating it as a medical emergency with admission to a specialist stroke unit, and receiving the best professional treatment could significantly improve outcomes.
Take action to prevent stroke or heart attack :
1. Monitor the high blood pressure – Understanding and managing blood pressure with changes in lifestyle or medicine will reduce the stroke risk.
2. Do moderate exercises five times a week-Over 1/3 of all strokes happen to people who do not exercise regularly.
3. Eat a healthy, balanced diet-Nearly a quarter of strokes are associated with poor diet, especially low fruit and vegetable consumption. To reduce your risk of stroke, eat five or more portions of fruit and vegetables and low intake of salt.
4. Maintain a healthy weight (Body mass index (BMI) or waist-to-hip ratio)-Obesity is associated
with almost 1 in 5 strokes.
5. Reduce the cholesterol-More than 1 in 4 strokes is associated with elevated 'bad' cholesterol (LDL) levels. Instead of saturated fats consume high saturated non-
hydrogenated fats. If diet alone is not feasible, consult your doctor on medicine.
6. Stop smoking – More than 1 in 10 strokes are associated with smoking. Stopping smoking will lower the stroke risk. Getting assistance in quitting increases your chances of success.
7. Reduce alcohol intake – More than 1 million strokes are associated with excessive consumption
of alcohol each year. Reducing the intake of alcohol can help reduce the risk of stroke.
8. Identify and treat atrial fibrillation-9 percent of strokes are associated with an irregular
heartbeat or other heart condition. Talk to your doctor about treatment options to mitigate the
risk.
9. Diabetes control/prevention of diabetes as diabetes raises stroke risk. Talk to your doctor about
improvements in care and lifestyle to regulate diabetes if you have diabetes; and reduce your
risk of stroke.
10. Stroke awareness-Fair access to health care and health education will have a positive impact on reducing stroke and other non-communicable diseases.

